|
Light Dependent
Resistors (LDRs)
Objectives:
| • Understand how a light-dependent resistor (LDR)
works. • Be able to describe the
relationship between resistance and light intensity for an LDR.
• Be able to describe applications of LDRs.
|
 |
Task 1 - Starter
Remind the person next to you:
• The relationship between voltage and current for a
resistor.
• The relationship between temperature and resistance for a
bulb.
• The relationship between temperature and resistance for a
thermistor.
Task 2
| You are going to investigate how the
resistance of an LDR changes with light intensity. Your
teacher will give you a multimeter and an LDR. You will
need to collect a ray box, power supply, a multimeter and some
leads. Test the resistance of the LDR as you increase the
voltage of the lamp from 0V to 12V. You will need to
draw a suitable table to collect your results. |
 |
| Voltage
across lamp (V) |
Resistance of LDR (kΩ) |
| 0 |
|
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
|
 |
Task 3
Plot a graph of your results.
• Lamp voltage should be along the x-axis.
• Resistance should be along the y-axis.
• Both the axes should have labels and units.
• Give your graph a suitable title.
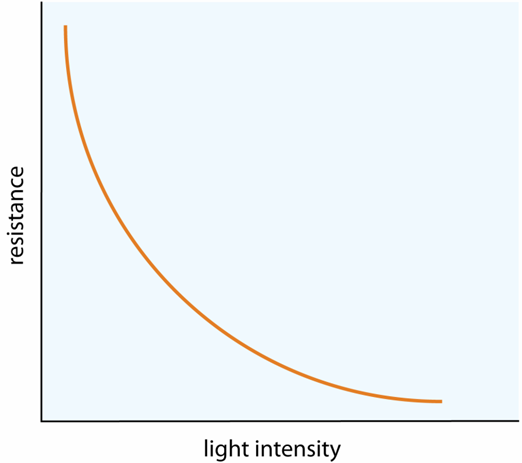
Your graph should look
something like this!
Task 4
Listen carefully as your teacher shows you
this presentation, and explains why an LDR behaves like this.
Homework/Extension:
Find out at least 3 places that thermistors are used to
control or measure temperature. Write a sentence to explain how the
thermistor is used for each application.
Find out at least 3 places that LDRs are used to control or
measure light intensity. Write a sentence to explain how the LDR is used
for each application.
|

